Residential electrical wiring is a critical aspect of any home, serving as the backbone of the power system that keeps modern living possible. As a homeowner, understanding the basics of electrical wiring is not only essential for your safety but also empowers you to take charge of your home’s electrical maintenance and minor repairs. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeper into the fundamental principles of residential electrical wiring, covering key topics such as electrical circuits, components, safety precautions, and common troubleshooting techniques. Whether you’re a new homeowner eager to learn or an experienced one looking to expand your knowledge, this article will provide you with a solid foundation to confidently navigate your home’s electrical system.

Understanding Electrical Circuits:
Electrical circuits can be likened to the bloodstream of your home, allowing electricity to flow and power all your electrical appliances and devices. Here are some key concepts to grasp when it comes to residential electrical circuits:
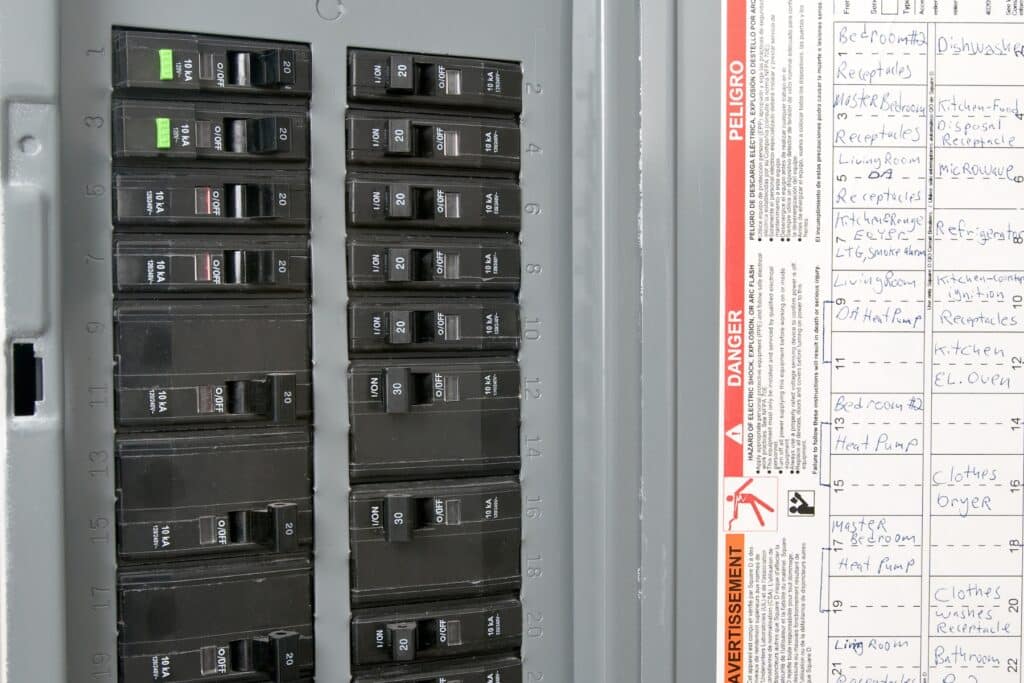
a) Main Service Panel: The main service panel, often located in a utility room or basement, is the heart of your home’s electrical system. It receives electrical power from the utility company through the service entrance cable and distributes it to various circuits throughout your house. Within the main service panel, circuit breakers act as gatekeepers, controlling the flow of electricity to each circuit.
b) Circuit Breakers: Circuit breakers are crucial safety devices designed to protect your home from electrical overloads and hazards. When a circuit experiences an excessive current flow, the circuit breaker “trips,” instantly interrupting the electrical supply to prevent damage and potential fires. Each circuit in your home has its dedicated circuit breaker, ensuring that if one circuit experiences a fault, it won’t affect the others.

c) Wiring: Residential wiring consists of different types of cables, each serving specific purposes. Non-metallic sheathed cable (NM) is commonly used for interior wiring, while armored cable (AC) offers added protection in areas where the wiring may be exposed to mechanical damage. Conduit, available in metal or plastic, is employed in more hazardous or outdoor environments, providing an extra layer of protection for the wiring within. Components of Residential Electrical Systems: Understanding the various components of your home’s electrical system is vital in maintaining and troubleshooting potential issues that may arise:
a) Outlets and Switches: Electrical outlets and switches are ubiquitous components found in every room. Outlets provide the connection points where you plug in your electronic devices, while switches control lighting fixtures. Familiarizing yourself with the different types of outlets, including grounded outlets and GFCI outlets (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters), ensures your electrical safety and enhances the functionality of your home.
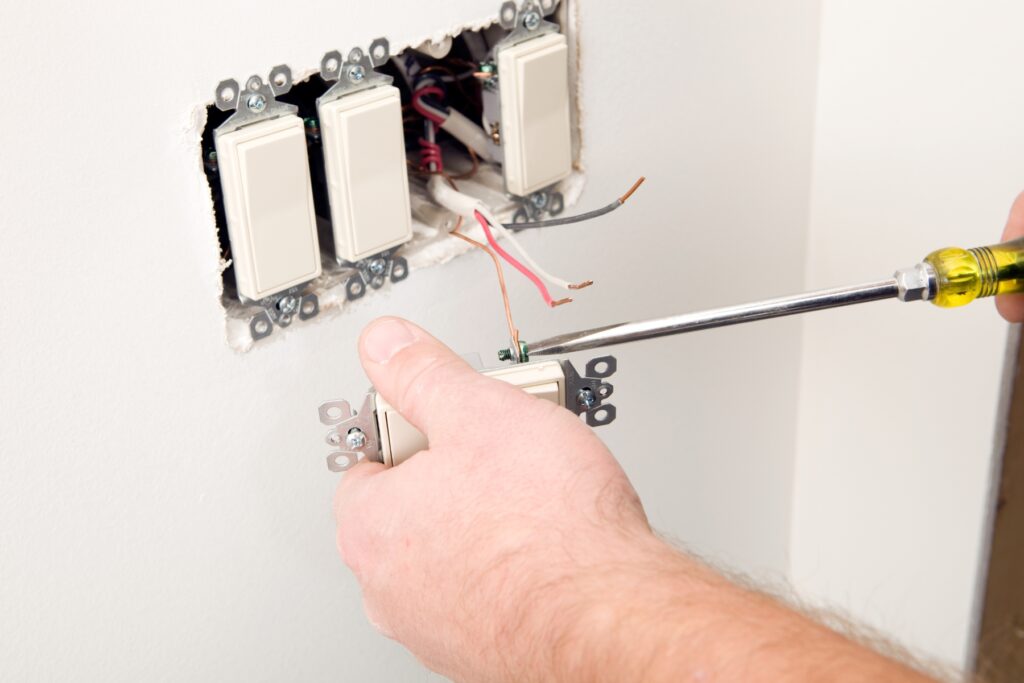

b) Light Fixtures: Light fixtures add both illumination and ambiance to your living spaces. Whether it’s a grand chandelier in your dining room or subtle recessed lighting in the kitchen, understanding how to install and connect light fixtures safely is essential for any homeowner.
c) Receptacles and Receptacle Wiring: Receptacles, or power outlets, are where the magic happens – powering your electronics, charging your devices, and running essential appliances. Learning about the proper installation techniques and troubleshooting common issues with receptacles is crucial to maintaining a functional electrical system. Safety Precautions: When dealing with electricity, safety should always be a top priority.
Here are some important safety precautions to keep in mind:
a) Electrical Inspections: Regular electrical inspections conducted by a licensed electrician are vital in identifying potential hazards and ensuring your home’s electrical system complies with safety standards. This proactive approach can prevent accidents and save you from costly repairs down the line.
b) Grounding and GFCI Protection: Proper grounding of electrical systems protects against electrical shock by providing a safe path for excess electrical current to flow into the earth. Additionally, Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI) outlets offer extra protection by instantly shutting off the power if they detect any ground faults, helping prevent electrical shocks in wet or hazardous areas like bathrooms and kitchens.
c) Overloading Prevention: Avoid overloading circuits by understanding their ampere rating (often marked on the circuit breaker) and distributing electrical loads evenly across different circuits. Overloading can cause circuits to trip frequently and potentially damage electrical devices. Troubleshooting Common Electrical Problems: Knowing how to troubleshoot common electrical issues can save you time, money, and the hassle of calling in a professional.
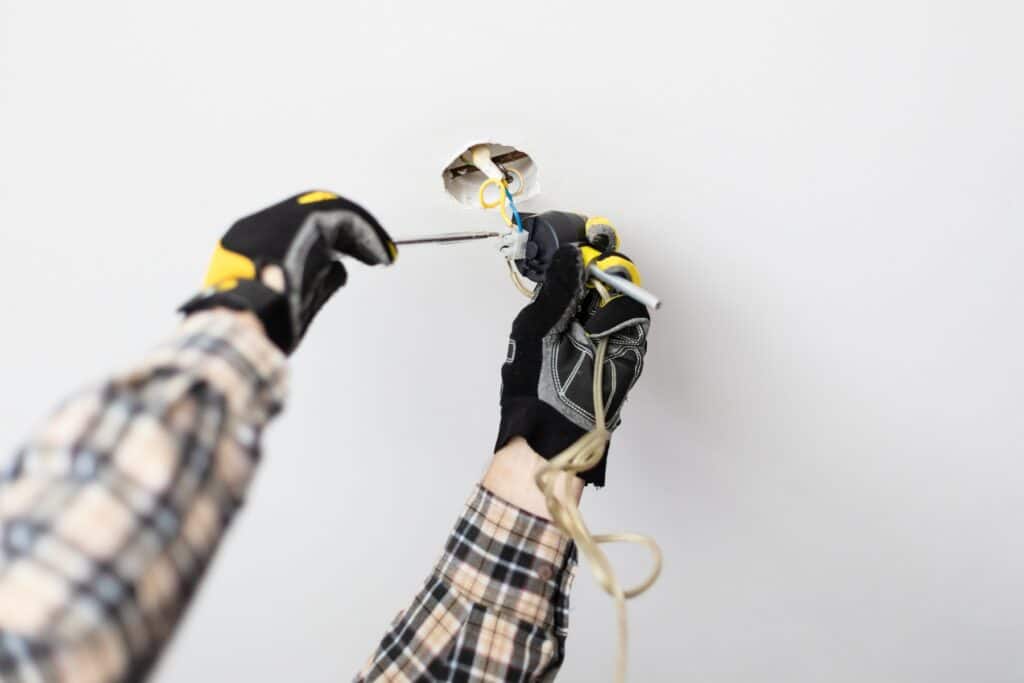

Here are a few common problems and their possible solutions:
a) Circuit Breaker Tripping: If a circuit breaker keeps tripping, it may be due to overloading or a short circuit. To resolve the issue, unplug any excessive load and identify and correct any damaged wiring.
b) Faulty Outlets or Switches: Malfunctioning outlets or switches may have loose connections or worn-out components. Replacing or tightening the connections can rectify the problem.
c) Flickering Lights: Flickering lights can be caused by loose bulbs, poor connections, or issues with the electrical circuit. Checking the bulb, tightening connections, or contacting an electrician can help resolve the problem. Conclusion: Understanding the basics of residential electrical wiring empowers homeowners to navigate their electrical systems confidently and ensures the safety of their homes. Armed with knowledge about electrical circuits, components, safety precautions, and common troubleshooting techniques, you are better equipped to take on small electrical projects and effectively communicate with professionals when needed. By being aware of electrical circuits, including the main service panel and circuit breakers, you can ensure a smooth flow of electricity throughout your home. Understanding different types of wiring, such as non-metallic sheathed cable (NM), armored cable (AC), and conduit, enables you to make informed decisions when it comes to installation and maintenance.
Being familiar with components like outlets, switches, light fixtures, and receptacles allows you to customize your home’s electrical setup to meet your needs. Whether you’re installing a new outlet, replacing a faulty switch, or connecting a beautiful light fixture, having a good grasp of the necessary procedures ensures safety and functionality.

Prioritizing safety precautions is paramount when dealing with electricity. Regular electrical inspections conducted by professionals provide peace of mind and identify potential hazards that may otherwise go unnoticed. Grounding your electrical system and utilizing GFCI outlets in appropriate areas add layers of protection against electrical shocks. Understanding the importance of load distribution helps prevent circuit overloading, maintain the integrity of your electrical system, and avoid damage to your appliances.
When faced with common electrical problems like tripping circuit breakers, faulty outlets or switches, and flickering lights, having troubleshooting skills can save you time and money. By following systematic approaches and knowing when to seek professional help, you can address these issues effectively and maintain a functional electrical system in your home.
In conclusion, residential electrical wiring is a fundamental aspect of homeownership. By understanding the basics of electrical circuits, components, safety precautions, and troubleshooting techniques, you gain confidence in managing your home’s electrical system. However, it’s important to note that complex electrical work should always be handled by licensed professionals. By prioritizing safety, acquiring knowledge, and knowing when to seek help, you can ensure the safety, functionality, and longevity of your home’s electrical system.